Plants are an essential part of our ecosystem, and they come in all shapes and sizes. Some plants grow faster than others, and this can be attributed to various factors such as light, soil quality, water, temperature, nutrients, and genetics.
Understanding why some plants grow faster than others can help you create an ideal environment for your plants to thrive.
The growth of plants is a complex process that is influenced by many factors. Photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy, is a critical factor in plant growth.
The amount of sunlight a plant receives can significantly impact its growth rate. Plants that receive more sunlight tend to grow faster than those that receive less. Similarly, the quality of soil and water can also impact plant growth. Nutrients and fertilizers play a crucial role in the growth of plants as well.
Genetic factors also play a significant role in plant growth. Different plants have different genetic makeups that determine how fast they grow and what conditions they require to thrive.
Understanding these genetic factors can help you choose the right plants for your environment and optimize their growth. In the following section, we will explore different factors that influence plant growth and ways to accelerate it.
Key Takeaways
- Plant growth is influenced by various factors such as light, soil quality, water, temperature, nutrients, and genetics.
- Photosynthesis is a critical factor in plant growth, and the amount of sunlight a plant receives can significantly impact its growth rate.
- Understanding genetic factors can help you choose the right plants for your environment and optimize their growth.
Related posts:
- Why Do Plants Have Two Photosystems Quizlet?
- How Cold Can a Snake Plant Survive?
- Why Do Plants And Animals Depend On Each Other?
Understanding Plant Growth

Plant growth is a complex process that involves the production of new cells and the initiation of new organs. It is influenced by various internal and external factors such as genetics, environment, nutrients, and water availability.
At the meristem level, growth is associated with the production of cells and initiation of new organs. Meristems are tissues that contain undifferentiated cells that can divide and differentiate into different cell types.
The apical meristem, located at the tip of the stem, is responsible for the growth in height of the plant. The lateral meristem, located at the base of the stem, is responsible for the growth in width of the plant.
Plant growth can be divided into two phases: cell division and cell elongation. During the cell division phase, cells divide rapidly, leading to an increase in the number of cells. During the cell elongation phase, cells elongate, leading to an increase in the size of the plant.
The rate of plant growth is influenced by various factors such as genetics, environment, nutrients, and water availability. For example, plants with favorable genetics may have a faster growth rate than plants with unfavorable genetics.
Similarly, plants grown in favorable environments with adequate nutrients and water availability may have a faster growth rate than plants grown in unfavorable environments with inadequate nutrients and water availability.
Role of Light and Photosynthesis
Sunlight
Sunlight is critical for plant growth and development. It provides the energy needed for photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose.
Different plants require different levels of sunlight to grow optimally. Some plants, such as succulents, can thrive in bright, direct sunlight, while others, such as ferns, prefer indirect or filtered light.
Photosynthesis
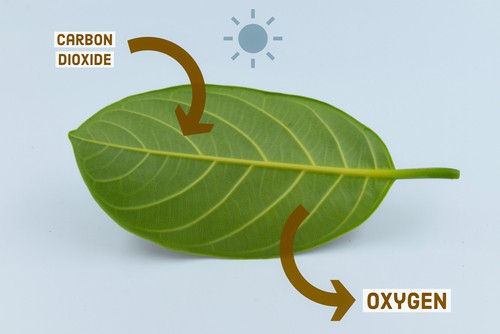
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen. The process occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells and is divided into two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions.
During the light-dependent reactions, light energy is absorbed by pigments in the plant, which then convert it into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. These molecules are used during the light-independent reactions to produce glucose from carbon dioxide.
The efficiency of photosynthesis can vary between different plant species. Some plants, such as corn and sugarcane, are known for their high photosynthetic efficiency, while others, such as soybeans and wheat, have lower efficiency.
Factors that can affect photosynthetic efficiency include the amount of sunlight, water availability, and the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air.
Importance of Soil and Water
Soil
Soil is one of the most important factors in plant growth. The type of soil, its texture, and nutrient content all play a crucial role in determining how well a plant will grow.
Different plants require different types of soil, and some plants are more adaptable to different soil types than others. For example, some plants thrive in sandy soil, while others prefer clay soil.
Soil texture is also important. Sandy soil drains quickly, which can be great for plants that don’t like to be waterlogged. On the other hand, clay soil retains water for longer periods, which can be beneficial for plants that require a lot of moisture.
Loamy soil, which is a mixture of sand, silt, and clay, is generally considered the best type of soil for most plants.
The nutrient content of the soil is also important. Plants require a variety of nutrients to grow, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. If the soil is lacking in any of these nutrients, the plant may not grow as well as it could. Adding fertilizer can help to improve the nutrient content of the soil and promote healthy plant growth.
Water Content

Water is another essential factor in plant growth. Plants require water to transport nutrients throughout their system and to photosynthesize. The amount of water a plant needs depends on a variety of factors, including the type of plant, the soil type, and the climate.
If a plant doesn’t receive enough water, it can become dehydrated and wilt. If it receives too much water, it can become waterlogged and drown. The key is to find the right balance. One way to do this is to water the plant deeply but infrequently, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between waterings.
In addition to the amount of water, the quality of the water is also important. Water that is too alkaline or acidic can be harmful to plants. Testing the pH of the water and adjusting it if necessary can help to ensure that the plant is receiving the right type of water.
Nutrients and Fertilizers
Nutrients
Plants require a range of nutrients to grow, including carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, potassium, calcium, and magnesium. These nutrients are absorbed from the soil and the air. The amount and type of nutrients required by a plant depends on its species and growth stage.
Nitrogen is a crucial nutrient for plant growth, as it is a component of chlorophyll, which is essential for photosynthesis. Iron is another important nutrient, as it is required for the production of chlorophyll.
Phosphorus is needed for root development and flower formation, while potassium helps regulate water balance and improve disease resistance.
Fertilizers
Fertilizers are a way to supplement the nutrients in the soil and help plants grow faster and healthier. Fertilizers come in different forms, including organic and inorganic. Organic fertilizers are made from natural sources, such as compost, manure, and bone meal, while inorganic fertilizers are synthetic and made from chemicals.
Most fertilizers supply nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as these are the most important nutrients for plant growth. However, different plants have different nutrient requirements, and it is important to choose a fertilizer that matches the needs of the plant.
Overuse of fertilizers can lead to nutrient imbalances, which can harm plants and the environment. It is important to follow the instructions on the fertilizer package and not to apply too much fertilizer.
The Effect of Temperature

Temperature is one of the most important environmental factors affecting plant growth. The optimal temperature for plant growth varies depending on the species. Some plants thrive in cooler temperatures, while others prefer warmer temperatures. However, extreme temperatures can be detrimental to plant growth.
When the temperature is too low, plant growth slows down, and the plant may even die. On the other hand, when the temperature is too high, the plant may suffer from heat stress, which can cause wilting, leaf drop, and even death. Therefore, it is important to maintain a suitable temperature range for the specific plant species.
Temperature affects several plant growth processes, such as transpiration, photosynthesis, respiration, germination, and flowering.
Whenever the temperature of an area increases to a certain degree, the processes mentioned earlier increase. Therefore, when it combines with day length, the temperature can affect the change from vegetative to reproductive growth.
Table 1 shows the optimal temperature range for some common plant species:
| Plant Species | Optimal Temperature Range |
| Tomato | 18-29°C |
| Lettuce | 16-20°C |
| Corn | 21-29°C |
| Peppers | 21-29°C |
| Cucumber | 21-29°C |
As seen in Table 1, the optimal temperature range for different plant species varies. For example, tomatoes grow best in temperatures between 18-29°C, while lettuce prefers cooler temperatures between 16-20°C. Therefore, it is important to know the specific temperature requirements of the plant species being grown.
Genetic Factors
Plants’ genetics play a significant role in determining their growth rate. Two main genetic factors that affect plant growth are the strain and mutations.
Same Strain

Plants that come from the same strain tend to grow at similar rates. This is because they have nearly identical genetic material. When plants of the same strain are grown in the same environment, they will have similar growth rates, as their genes are programmed to respond similarly to the environmental conditions.
However, there can still be slight variations in growth rate due to small genetic differences that can occur during mitotic divisions.
Mutation
Mutations can occur naturally or through genetic modification and can lead to significant changes in plant growth rates. Mutations can create new genes or alter existing ones, leading to changes in the plant’s physical characteristics. These changes can either positively or negatively affect the plant’s growth rate.
For example, a mutation that leads to a faster cell division rate can result in a faster-growing plant, while a mutation that affects the plant’s ability to absorb nutrients can result in a slower-growing plant.
Mutations can also occur during sexual reproduction, where genetic material from the male and female plants combine. This can result in a new strain with different growth characteristics than either of the parent strains.
Germination and Seedlings
Germination is the process by which a plant grows from a seed. Some seeds germinate faster than others due to various factors such as temperature, moisture, and light. Germination rates vary widely depending on the plant species and environmental conditions.
Germination Rates
Each plant species has a specific germination rate, which is the percentage of seeds that successfully sprout. Some seeds have a high germination rate, while others have a low germination rate. For example, lettuce seeds have a high germination rate, while parsley seeds have a low germination rate.
Temperature and moisture are the two most critical factors that affect germination rates. Most seeds germinate best in warm, moist soil. If the soil is too cold or too dry, the seeds will not germinate. Some seeds, such as wildflowers, require a cold period to break their dormancy and germinate.
Transplant

Once the seeds have germinated, they develop into seedlings. Seedlings are young plants that are not yet mature enough to survive on their own. They require care and attention to grow into healthy, mature plants.
Transplanting is the process of moving seedlings from their original container to a larger one or directly into the ground. Transplanting allows the seedlings to grow larger and develop a stronger root system. It also allows the seedlings to adapt to their new environment and grow stronger.
When transplanting seedlings, it is important to handle them carefully to avoid damaging the roots. The new container or planting hole should be large enough to accommodate the seedling’s root system. It is also important to water the seedling immediately after transplanting to prevent it from drying out.
Research and Findings
Researchers have been studying the factors that affect plant growth for decades. Through their research, they have discovered that several factors can impact a plant’s growth rate, including genetics, environmental conditions, and the availability of nutrients.
One study found that some plants can grow faster under stressful conditions. Researchers at Stanford University found that Schrenkiella parvula grows faster under stressful conditions because it produces less of a stress hormone that acts like a stop signal for growth.
This finding is significant because it challenges the common belief that stress is always harmful to plants.
Another study found that some plants are better at photosynthesis than others. RuBisCO is responsible for catalyzing carbon dioxide-fixation in photosynthesis.
Researchers have discovered that some plants have more efficient RuBisCO than others, which allows them to grow faster and more efficiently. This finding suggests that improving the efficiency of RuBisCO could help increase crop yields and reduce the amount of land needed for agriculture.
Additionally, researchers have discovered that some plants are better at cooperating with beneficial fungi than others. Some plants grow slowly but enjoy a long life by cooperating with beneficial fungi. Others grow fast but are initially more vulnerable to disease and other environmental stresses.
Ways to Accelerate Growth
There are several ways to accelerate plant growth. Here are some tips to help plants grow faster:
1. Provide Adequate Light

Plants need light to grow. If they don’t get enough light, they will grow slowly. Place plants in a location where they can get enough sunlight or use grow lights to provide additional light.
2. Give Plants Enough Water
Water is essential for plant growth. Plants that don’t get enough water will grow slowly or die. Be sure to water plants regularly and provide enough water to keep the soil moist but not waterlogged.
3. Use Fertilizer
Fertilizer provides plants with the nutrients they need to grow. Use a balanced fertilizer or one that is specific to the type of plant you are growing. Be careful not to over-fertilize, as this can damage plants.
4. Prune Plants
Pruning plants can help them grow faster. Removing dead or damaged leaves and branches can encourage new growth. Pruning can also help control the size and shape of the plant.
5. Provide TLC
Plants that are well cared for will grow faster than those that are neglected. Provide plants with the right environment, including proper light, water, and temperature. Remove any dead or damaged leaves and provide support for plants that need it.
By following these tips, it is possible to accelerate plant growth and help plants reach their full potential.
Understanding Different Types of Plants
Plants come in various shapes, sizes, and colors. Some grow tall and fast, while others grow slowly and stay small. Understanding different types of plants can help you determine how to care for them and why they may grow at different rates.
Perennials
Perennials are plants that live for more than two years. They usually grow slowly and steadily, taking their time to mature. Some perennials, like trees, can take decades to reach their full height and size. This is because they invest more energy into their root systems, which helps them survive harsh weather conditions and droughts.
Other perennials, like shrubs and bushes, grow faster than trees but still take several years to reach their full size. They usually have a woody stem and produce flowers or fruits. Perennials are known for their longevity, but they also require more maintenance than annuals or biennials.
Flowers

Flowers are a popular type of plant that come in a variety of colors and shapes. They are usually annuals or biennials, which means they complete their life cycle in one or two years. Flowers grow quickly and produce colorful blooms that attract pollinators like bees and butterflies.
Annuals are plants that complete their life cycle in one year. They grow quickly from seed, produce flowers, and then die when the weather turns cold. Biennials, on the other hand, take two years to complete their life cycle. They grow slowly in their first year, produce leaves, and then bloom in their second year before dying.
Flowers require regular watering and fertilization to grow and bloom. They also need to be pruned and deadheaded to encourage new growth and prevent diseases.
Understanding the different types of plants can help you determine how to care for them and why they may grow at different rates. Whether you are growing perennials or flowers, it is important to give them the proper care and attention they need to thrive.
The Role of the Root System
The root system is an essential part of a plant’s growth and development. It serves as the anchor for the plant, keeping it stable in the soil. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in nutrient and water uptake. Some plants have more extensive root systems than others, which can contribute to their faster growth rate.
Root systems can be classified into two types: taproot and fibrous. Taproot systems have a primary root that grows deep into the soil, with smaller lateral roots branching off of it. Fibrous root systems, on the other hand, have many small, shallow roots that spread out in all directions.
Plants with taproot systems, such as carrots and radishes, tend to grow slower than those with fibrous root systems, such as grasses and clovers. This is because taproot systems require more energy to grow and maintain, and they are less efficient at absorbing nutrients and water from the soil.
In contrast, fibrous root systems have a larger surface area, which allows them to absorb more nutrients and water from the soil. This increased efficiency can contribute to faster plant growth. Additionally, fibrous root systems are better at preventing soil erosion, as they hold the soil in place more effectively.
The Effect of Pot and Outdoors
1. Pot
The type of pot in which a plant is grown can have a significant effect on its growth rate. Plants grown in smaller pots will have less room for root growth, which can lead to stunted growth and lower yields.
Conversely, plants grown in larger pots will have more room for root growth, allowing them to absorb more nutrients and water, which can lead to faster growth and higher yields.
It’s important to note that the type of potting mix used can also impact plant growth. A mix that is too dense or compacted can hinder root growth, while a mix that is too light or airy can dry out too quickly, leading to water stress for the plant.
2. Outdoors

Plants grown outdoors are subject to a wide range of environmental factors that can impact their growth rate. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and sunlight can all play a role in determining how quickly a plant grows.
For example, plants grown in cooler temperatures may grow more slowly than those grown in warmer temperatures. Similarly, plants grown in areas with high humidity may be more susceptible to mold and other fungal diseases, which can slow their growth rate.
Sunlight is also a critical factor in plant growth. Plants require a certain amount of light to photosynthesize and produce energy, and different plants have different light requirements. Some plants, such as tomatoes and peppers, require full sun to grow and produce fruit, while others, such as leafy greens, can tolerate partial shade.
3. Lead
It’s worth noting that lead contamination in soil can also impact plant growth. Lead is a toxic heavy metal that can accumulate in soil over time, and exposure to lead can lead to stunted growth, reduced yields, and other health problems for plants.
If you suspect that your soil may be contaminated with lead, it’s important to have it tested before planting. In some cases, it may be necessary to remediate the soil or use raised garden beds to avoid contact with contaminated soil.
Fitness in Plants
Plants are living organisms that have evolved over millions of years to survive in their environment. Their fitness is determined by how well they can adapt to changes in their surroundings. Fitness in plants is a measure of their ability to survive and reproduce in their environment.
Plant fitness is influenced by many factors, including genetics, environment, and competition. Plants with favorable genetic traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on those traits to their offspring.
The environment also plays a significant role in plant fitness. Plants that are better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce than those that are not.
One of the most important factors that influence plant fitness is their ability to photosynthesize. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into energy. Plants that can photosynthesize more efficiently are more likely to survive and reproduce than those that cannot.
Another factor that affects plant fitness is their ability to absorb nutrients from the soil. Plants that have a better root system and can absorb nutrients more efficiently are more likely to survive and reproduce.
The availability of water also plays a critical role in plant fitness. Plants that can withstand drought conditions and use water more efficiently are more likely to survive and reproduce.
In addition to genetics and environment, competition also plays a significant role in plant fitness. Plants that can compete more effectively for resources such as sunlight, water, and nutrients are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Some plants have developed mechanisms to outcompete other plants, such as growing taller or developing larger leaves to capture more sunlight.
Frequently Asked Questions

How can environmental factors affect the growth rate of plants?
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light can significantly affect the growth rate of plants. For example, high temperatures can cause plants to wilt, while low temperatures can slow down their growth.
Similarly, low humidity can cause plants to dry out, while high humidity can lead to fungal growth. Light is also a critical factor in plant growth, as it is essential for the process of photosynthesis.
What are some techniques to promote faster plant growth?
There are several techniques that can be used to promote faster plant growth. One of the most effective ways is to provide plants with optimal growing conditions, including proper lighting, water, and nutrients.
Another technique is to prune plants regularly, which can encourage new growth and improve their overall health. Additionally, using fertilizers or other growth-promoting products can help stimulate plant growth.
What role do nutrients play in plant growth?
Nutrients are essential for plant growth, as they provide the building blocks necessary for the development of leaves, stems, and roots. The three primary nutrients that plants require are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Nitrogen is necessary for the development of leaves and stems, while phosphorus is essential for root development. Potassium helps regulate water balance in plants and is essential for flower and fruit development.
How do different plant species adapt to their environment to grow faster?
Different plant species have evolved unique strategies to adapt to their environment and grow faster. For example, some plants have developed deep root systems that can access water and nutrients deep within the soil.
Others have evolved specialized leaves that are better adapted to capturing sunlight. Additionally, some plants have developed mechanisms to protect themselves from predators or harsh environmental conditions.
What is the impact of light on plant growth?
Light is critical for plant growth, as it is necessary for the process of photosynthesis. Different plants require different levels of light, depending on their species and growing conditions.
For example, some plants require full sunlight to grow, while others prefer partial shade. Additionally, the quality of light can also affect plant growth, with some plants responding better to certain wavelengths of light.
How does the age of a plant affect its growth rate?
The age of a plant can significantly affect its growth rate. Generally, younger plants grow faster than older plants, as they have more energy and resources available for growth.
However, as plants mature, their growth rate typically slows down, and they may require more nutrients and care to maintain their health. Additionally, some plants have specific growth stages where they may experience rapid growth, followed by a period of slower growth.

Hey, I’m Lisa and I’ve been an avid gardener for over 30 years. I love writing, talking and living in the garden! Feel free to connect with me on my socials below


