Plants are autotrophic organisms that produce their food through the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process is essential for the survival of plants and other living organisms on earth.
The process of photosynthesis involves several steps and requires specific plant parts to function correctly. The leaves are the primary site of photosynthesis, and they contain chloroplasts, which are responsible for capturing light energy. The stem and roots also play vital roles in photosynthesis by providing support, nutrients, and water to the plant.
To carry out photosynthesis, plants require specific raw materials. The primary raw materials are carbon dioxide and water, which are obtained from the atmosphere and soil, respectively.
Plants also require light energy, which is absorbed by the chlorophyll pigment in the chloroplasts. The process of photosynthesis also requires several enzymes and coenzymes to function correctly.
Key Takeaways on Where Do Plants Get Raw Materials for Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
- The primary site of photosynthesis is the leaves, while the stem and roots provide support, nutrients, and water to the plant.
- The raw materials required for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide, water, and light energy, and the process also requires several enzymes and coenzymes to function correctly.
Check out these other popular picks in this category:
- Where Can You Find The Num Num Plant?
- When to Plant Grass Seed in Idaho?
- Where Can I Get a Jasmine Plant?
The Process of Photosynthesis
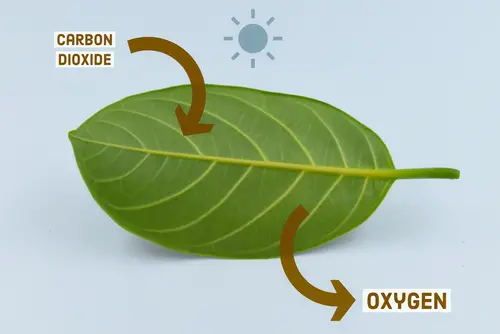
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants produce food using light energy, water, and carbon dioxide. The process is divided into two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle.
Light-Dependent Reactions
The light-dependent reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts. During this stage, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll, which excites electrons. These electrons are then passed through a series of electron carriers, releasing energy that is used to produce ATP and NADPH.
The light-dependent reactions also produce oxygen as a byproduct. Water molecules are split in a process called photolysis, releasing electrons, protons, and oxygen. The oxygen is released into the atmosphere, while the electrons and protons are used to produce ATP and NADPH.
Calvin Cycle
The Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma of the chloroplasts. During this stage, carbon dioxide is fixed into organic molecules using the energy from ATP and NADPH produced during the light-dependent reactions.
The first step of the Calvin cycle is carbon fixation, where carbon dioxide is combined with a five-carbon sugar called ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) to form a six-carbon molecule. This molecule is then broken down into two three-carbon molecules called 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG).
The 3PG molecules are then converted into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P), which can be used to produce glucose and other organic molecules. Some of the G3P molecules are also recycled to regenerate RuBP, which is necessary for the continuation of the cycle.
Role of Different Plant Parts
Photosynthesis is a complex process that involves different plant parts working together to produce energy. In this section, we will discuss the role of different plant parts in photosynthesis.
Leaves and Chloroplasts
Leaves are the primary site of photosynthesis in plants. The green pigment called chlorophyll is present in the chloroplasts of the mesophyll cells of leaves. Chloroplasts are the organelles that carry out photosynthesis. They contain the necessary components such as pigments, enzymes, and electron carriers required for the process.
During photosynthesis, light energy is captured by chlorophyll and converted into chemical energy. This energy is then used to produce glucose from carbon dioxide and water. The glucose is then transported to other parts of the plant to be used as a source of energy.
Roots and Stems

While leaves are the primary site of photosynthesis, roots and stems also play a crucial role. Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil, which are required for photosynthesis. Stems transport water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves.
Stomata are small openings present on the surface of leaves that allow for the exchange of gases. Carbon dioxide enters the leaf through these openings, while oxygen and water vapor exit. Guard cells are specialized cells that regulate the opening and closing of stomata.
In summary, leaves and chloroplasts are the primary sites of photosynthesis, while roots and stems play a crucial role in providing water and nutrients to the plant. Stomata and guard cells regulate the exchange of gases that are required for photosynthesis.
Raw Materials for Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy. During this process, plants use raw materials to produce glucose (sugar) and oxygen. The raw materials required for photosynthesis are water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight.
Water and Minerals
Water is an essential raw material for photosynthesis. It is absorbed by plants through their roots from the soil. The water is then transported through the plant’s vascular system to the leaves, where it is used in photosynthesis.
Minerals, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are also absorbed by the plant’s roots from the soil and used in photosynthesis. These minerals help in the production of chlorophyll, which is essential for photosynthesis.
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a gas that is found in the atmosphere. It is a critical raw material for photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide through small pores called stomata, which are present on the leaves. The carbon dioxide is then used along with water and sunlight to produce glucose and oxygen.
In conclusion, water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight are the raw materials required for photosynthesis. Water is absorbed by plants from the soil, while carbon dioxide is obtained from the atmosphere. Minerals present in the soil are also used by plants to produce chlorophyll, which is necessary for photosynthesis.
Products of Photosynthesis
During photosynthesis, plants convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose and oxygen. The raw materials for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water, which are taken up by the plant from the surrounding environment.
The products of photosynthesis are essential for the survival of the plant and for other living organisms that depend on them for energy.
Oxygen

One of the main products of photosynthesis is oxygen. During the process, plants take in carbon dioxide and water and use energy from sunlight to convert them into glucose and oxygen.
The oxygen produced during photosynthesis is released into the atmosphere, where it is used by animals and other organisms for respiration. In fact, the oxygen produced by photosynthesis is responsible for maintaining the oxygen levels in the Earth’s atmosphere, which is essential for the survival of most living organisms.
Glucose
Another important product of photosynthesis is glucose. Glucose is a simple sugar that is used by the plant as a source of energy for growth and other metabolic processes.
During photosynthesis, plants use energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose. The glucose produced during photosynthesis is stored in the plant’s cells and used as a source of energy for growth and other metabolic processes.
Importance of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a vital process for the survival of living organisms on Earth. It is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, which they use to produce food, oxygen, and other essential organic compounds.
Photosynthesis is crucial for the maintenance of life on Earth, and it has several important benefits.
Food Production
Photosynthesis is the primary source of food for most organisms on Earth. Plants use the energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, a type of sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for all living organisms.
The glucose produced during photosynthesis is used to produce other organic compounds, such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, which are essential for the growth and development of plants and animals.
Oxygen Production
Photosynthesis is also responsible for the production of oxygen, which is essential for the survival of most living organisms, including humans. During photosynthesis, plants release oxygen as a byproduct, which is then used by animals and humans for respiration.
Oxygen is necessary for the production of energy in cells, and without it, most organisms would not be able to survive. In addition to food and oxygen production, photosynthesis has several other benefits. It helps to regulate the Earth’s climate by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and releasing oxygen.
It also helps to maintain the balance of nutrients in the soil by fixing nitrogen, a process by which plants convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that can be used by other organisms.
Adaptations in Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process that is vital for life on Earth. It is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy that can be used by living organisms. In order to carry out photosynthesis, these organisms require raw materials such as carbon dioxide and water.
Chlorophyll Variations
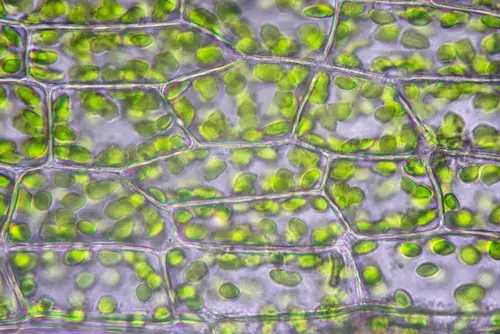
Chlorophyll is a pigment that is essential for photosynthesis. It is responsible for capturing light energy and converting it into chemical energy. There are several variations of chlorophyll, including chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, chlorophyll c, and chlorophyll d.
Chlorophyll a is the most common form of chlorophyll and is found in all photosynthetic organisms. Chlorophyll b is found in green algae and in the leaves of higher plants.
Chlorophyll c is found in brown algae and diatoms. Chlorophyll d is found in red algae. The different forms of chlorophyll allow photosynthetic organisms to absorb light at different wavelengths, which allows them to carry out photosynthesis in different environments.
Photosynthetic Organisms
Photosynthesis is carried out by a variety of organisms, including plants, algae, and some bacteria. Photoautotrophs are organisms that can produce their own food using light energy. Plants, green algae, and cyanobacteria are examples of photoautotrophs.
Algae are a diverse group of organisms that can carry out photosynthesis. They can be found in a variety of environments, including freshwater, saltwater, and soil. Some algae are unicellular, while others are multicellular. Algae can be green, red, or brown, depending on the type of chlorophyll they contain.
Bacteria are also capable of carrying out photosynthesis. Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, are a type of bacteria that carry out photosynthesis. They are found in a variety of environments, including freshwater, saltwater, and soil. Cyanobacteria are important contributors to the global carbon cycle and are also capable of fixing nitrogen.
Environmental Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a complex process that is affected by various environmental factors. Understanding these factors can help us optimize plant growth and increase crop yields. The three main factors that affect photosynthesis are light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature.
Light Intensity
Light is the primary source of energy for photosynthesis. As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis also increases. However, there is a limit to how much light a plant can absorb. If the light intensity becomes too high, the plant may suffer from photoinhibition, which can damage the photosynthetic machinery.
Carbon Dioxide Concentration
Carbon dioxide is another essential raw material for photosynthesis. As the concentration of carbon dioxide increases, the rate of photosynthesis also increases.
However, there is a limit to how much carbon dioxide a plant can absorb. If the concentration becomes too high, the plant may suffer from carbon dioxide toxicity, which can damage the photosynthetic machinery.
Temperature

Temperature is also an important factor that affects photosynthesis. As temperature increases, the rate of photosynthesis also increases. However, there is an optimum temperature range for photosynthesis.
If the temperature becomes too high or too low, the plant may suffer from heat or cold stress, which can damage the photosynthetic machinery.
In addition to these three factors, other environmental factors can also affect photosynthesis. For example, climate and time of day can affect the availability of light and carbon dioxide. Water availability can also affect photosynthesis, as water is needed for the photosynthetic machinery to function properly.
The Cellular Level of Photosynthesis
Cellular Organelles
Photosynthesis takes place within specialized organelles called chloroplasts located in the cells of plants, algae, and some bacteria. Chloroplasts are unique organelles that contain pigments such as chlorophyll, which absorb light energy, and carotenoids, which protect the chlorophyll from damage by excessive light.
The chloroplasts are surrounded by a double membrane, which encloses a fluid-filled matrix called the stroma. The stroma contains enzymes that are responsible for the synthesis of organic molecules during the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis.
Within the stroma, there are stacks of flattened sacs called thylakoids, which are interconnected to form a complex network called the grana. The thylakoids contain pigments that absorb light energy and electron transport chains that are involved in the conversion of light energy into chemical energy, which is stored in the form of ATP and NADPH.
Chemical Energy Conversion
Photosynthesis involves the conversion of light energy into chemical energy, which is stored in the form of ATP and NADPH. This process occurs in two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions.
During the light-dependent reactions, light energy is absorbed by the pigments in the thylakoid membranes, and the energy is used to generate ATP and NADPH. The ATP and NADPH are then used during the light-independent reactions to synthesize organic molecules such as glucose.
The light-independent reactions take place in the stroma of the chloroplasts and involve a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that use carbon dioxide, ATP, and NADPH to synthesize organic molecules such as glucose.
The process of photosynthesis is an essential source of organic molecules for all living organisms, and it is responsible for maintaining the oxygen and carbon dioxide balance in the Earth’s atmosphere.
Photosynthesis and the Carbon Cycle

Plants get the raw materials for photosynthesis from the environment. During photosynthesis, plants use energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. The carbon cycle plays a critical role in this process.
The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon moves through the environment. Photosynthesis by land plants, bacteria, and algae converts carbon dioxide or bicarbonate into organic molecules. Organic molecules made by photosynthesizers are passed through food chains, and cellular respiration converts the organic carbon back into carbon dioxide gas.
Carbon dioxide is a crucial component of the carbon cycle. It is a greenhouse gas that plays a significant role in climate change. During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) from the air and soil.
Within the plant cell, the water is oxidized, meaning it loses electrons, while the carbon dioxide is reduced, meaning it gains electrons. This transforms the water into oxygen and the carbon dioxide into glucose.
Respiration is the process by which organic compounds are broken down to release energy. During respiration, glucose is oxidized to produce energy, carbon dioxide, and water. This process releases the energy stored in the glucose molecule, which is then used by the plant to power its metabolic processes.
Organic matter is an essential component of the carbon cycle. When plants and animals die, their bodies are broken down by decomposers such as bacteria and fungi. During decomposition, organic matter is converted into carbon dioxide, water, and other inorganic compounds.
Carbonates are another important component of the carbon cycle. Carbonates are compounds that contain carbon and oxygen, such as calcium carbonate (CaCO3). They are found in rocks, soils, and ocean sediments. When carbonates are weathered or dissolved, they release carbon dioxide into the environment.
Photosynthesis and Human Population
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, which is stored in the bonds of organic molecules such as glucose. This process is essential for life on Earth as it is the primary source of oxygen and food that sustains the human population.
During photosynthesis, plants obtain raw materials such as carbon dioxide, water, and minerals from the environment.
Carbon dioxide is taken in through small openings called stomata on the leaves, and water is absorbed by the roots and transported to the leaves through a network of specialized cells. Minerals such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are also absorbed from the soil and transported to the leaves.
The raw materials are then used to produce glucose and oxygen through a series of chemical reactions that take place in specialized structures called chloroplasts. The glucose is used by the plant as a source of energy for growth and other metabolic processes, while oxygen is released into the atmosphere as a byproduct of photosynthesis.
The importance of photosynthesis in sustaining the human population cannot be overstated. Oxygen produced during photosynthesis is essential for human respiration, while glucose produced by plants is the primary source of energy for all living organisms, including humans.
As the human population continues to grow, the demand for oxygen and food also increases. This has led to increased pressure on the environment, including deforestation and pollution, which has the potential to negatively impact photosynthesis and the sustainability of the human population.
Conclusion

Plants are able to carry out photosynthesis, a process that converts light energy into chemical energy in order to produce glucose and oxygen. In order to carry out this process, plants require raw materials such as carbon dioxide, water, and minerals.
During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide from the air through small pores called stomata that are present on the leaves. Water is obtained from the soil through the roots and transported to the leaves through a vascular system.
Light energy is absorbed by the chlorophyll present in the chloroplasts of the plant cells, which is then used to convert the carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
It is important to note that the amount of raw materials required by the plant for photosynthesis varies depending on factors such as light intensity, temperature, and the availability of nutrients. For example, plants require more water during hot and dry conditions, while they require more carbon dioxide when light intensity is high.
In addition to the raw materials required for photosynthesis, plants also require other nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are obtained from the soil. These nutrients are essential for the growth and development of the plant, and their availability can affect the rate of photosynthesis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the four raw materials needed for photosynthesis and how are they obtained?
The four raw materials needed for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide, water, sunlight, and chlorophyll. Carbon dioxide is obtained from the air through tiny pores called stomata on the leaves.
Water is absorbed by the roots from the soil. Sunlight is absorbed by the chlorophyll in the leaves, and chlorophyll is a pigment that gives plants their green color.
What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis and how does it aid in the process?
Chlorophyll is a pigment that absorbs light energy from the sun. The energy is then used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen through the process of photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is found in the chloroplasts of plant cells, and it is essential for photosynthesis to occur.
What are the products of photosynthesis and how are they used by the plant?
The products of photosynthesis are glucose and oxygen. Glucose is a sugar that is used by the plant as a source of energy. It is also used to build other molecules that the plant needs, such as cellulose. Oxygen is released into the air as a byproduct of photosynthesis.
How do plants obtain carbon dioxide, one of the raw materials for photosynthesis?
Plants obtain carbon dioxide from the air through tiny pores called stomata on the leaves. The stomata open and close to allow carbon dioxide to enter the plant and oxygen to exit.
Where and how do plants obtain water, another raw material for photosynthesis?
Plants obtain water from the soil through their roots. The roots absorb water and minerals from the soil and transport them to the leaves where photosynthesis occurs.
What parts of the plant are involved in collecting the raw materials for photosynthesis?
The leaves are the primary site of photosynthesis in plants. They contain chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy from the sun. The stomata on the leaves allow carbon dioxide to enter the plant and oxygen to exit.
The roots of the plant absorb water and minerals from the soil and transport them to the leaves where photosynthesis occurs.

Hey, I’m Lisa and I’ve been an avid gardener for over 30 years. I love writing, talking and living in the garden! Feel free to connect with me on my socials below

